Renewable energy technology has become increasingly prevalent in our modern world as we seek cleaner and more sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. Harnessing the power of natural resources such as sunlight, wind, and water, renewable energy technologies offer a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Let’s delve into how these innovative technologies work and the essential role they play in shaping a greener future.
Solar Power:
One of the most well-known forms of renewable energy technology is solar power. Solar panels, typically installed on rooftops or in solar farms, capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the solar panels, the semiconductors within the panels absorb the photons, generating an electric current. This direct current (DC) electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) electricity, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire communities. The excess electricity generated can be stored in batteries for use during periods of low sunlight or fed back into the grid.
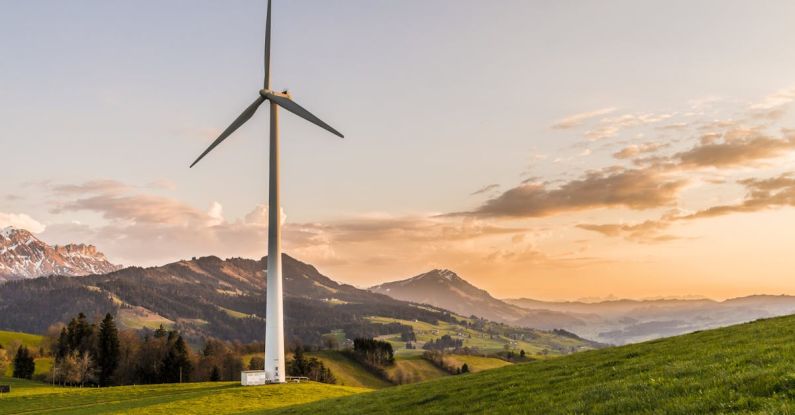
Wind Power:
Another prominent form of renewable energy technology is wind power. Wind turbines, often seen dotting landscapes or offshore in the ocean, harness the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. As the wind blows, it causes the turbine blades to rotate, which in turn spins a generator to produce electricity. The electricity generated is then transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses. Wind power has the advantage of being a scalable technology, with larger wind farms capable of generating significant amounts of electricity to meet the energy needs of entire regions.
Hydropower:
Hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, utilizes the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. Dams are constructed on rivers to create reservoirs of water at higher elevations. When the water is released from the reservoir, it flows through turbines, causing them to spin and generate electricity. Hydropower is a reliable and efficient form of renewable energy, providing a constant source of electricity that can be adjusted based on demand. However, concerns have been raised about the environmental impact of dams on ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
Biomass Energy:
Biomass energy involves the conversion of organic materials such as wood, crop residues, and agricultural waste into biofuels or biogas for energy production. Through processes such as combustion, gasification, or fermentation, biomass can be converted into heat, electricity, or transportation fuels. Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral since the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during photosynthesis. However, the sustainability of biomass energy depends on responsible sourcing practices to prevent deforestation and ensure the long-term availability of biomass resources.
Geothermal Energy:
Geothermal energy taps into the heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface to generate electricity and heat buildings. By drilling wells into geothermal reservoirs, hot water or steam is brought to the surface to drive turbines and produce electricity. Geothermal energy is a reliable and continuous source of power, making it well-suited for baseload electricity generation. Additionally, geothermal heat pumps can be used for heating and cooling buildings, offering energy-efficient solutions for residential and commercial spaces.
Innovations in Renewable Energy Technology:
Advancements in renewable energy technology continue to drive the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy system. From floating solar farms and offshore wind turbines to smart grids and energy storage solutions, innovative technologies are expanding the reach and efficiency of renewable energy sources. The integration of renewable energy with digital technologies and artificial intelligence is enabling more precise forecasting and optimization of renewable energy systems, enhancing their reliability and performance.
In conclusion, renewable energy technology is revolutionizing the way we generate and consume energy, offering a path towards a more sustainable future. By harnessing the power of natural resources such as sunlight, wind, water, biomass, and geothermal heat, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate the impacts of climate change. As we continue to innovate and invest in renewable energy technologies, we move closer to achieving a cleaner, greener, and more resilient energy system for future generations.